MTP2 and MTP3: Message Transfer Part level 2 and level 3
Posted on |
MTP2 and MTP3: Message Transfer Part level 2 and level 3
Message Transfer Part (MTP), a protocol in the SS7/C7 protocol suite, transfers signal messages and performs associated functions, such as error control and signaling link security. Message Transfer Part (MTP) also provides reliable routing within a network. MTP has two parts, MTP level 2 (MTP2) and level 3 (MTP3), that performs functions at the layers 2 and 3 respectively of the OSI 7 layers model.
Message Transfer Part Level 2 (MTP2) resides at Layer 2 in the SS7 protocol stack. It is responsible for the reliable transmission of signalling units over an individual Signalling Link. MTP2 reliability is achieved through retransmission techniques.
Message Transfer Part level 3 (MTP3) is the network layer in the SS7 protocol stack. It routes SS7 signalling messages to public network nodes by means of Destination Point Codes, and to the appropriate signalling entity within a node by means of a Service Info Octet. MTP3 is specified as part of the SS7 protocol and is also referred to as part of the B-ICI interface for ATM. MTP3 sits between MTP2 and the user parts (ISUP, TUP, SCCP and TCAP) of the SS7 protocol stack. B-ISUP is an Application Layer protocol run over MTP3.
MTP3 is split into two distinct parts, SMH (Signalling Message Handling) and SNM(Signalling Network Management). The SNM part looks after the general management of MTP, the SHM part deals with the discrimination, distribution and routing of signalling messages. MTP3 defines the functions and procedures of the signalling system for signalling message handling and signalling network management. Signalling message handling consists of the actual transfer of a signalling message and directing the message to the proper signalling link or user part. Signalling network management consists of controlling the signalling message routing and configuration of the signalling network facilities based on predetermined information and the status of the signalling network facilities.
MTP3 provides a connectionless message transfer system for passing information across a network. MTP3 includes a number of link-protection features, to allow automatic rerouting of signalling messages around broken signalling transfer points. It includes certain management functions for congestion control on signalling links.
MTP2 User Adaptation Layer (M2UA) is used to access MTP2 functions using SCTP (Streaming Control Transmission Protocol). MTP3 User Adaptation Layer (M3UA) is a protocol for supporting the transport of any SS7 MTP3-User signaling (e.g., ISUP, SCCP and TUP messages) over the IP Network.
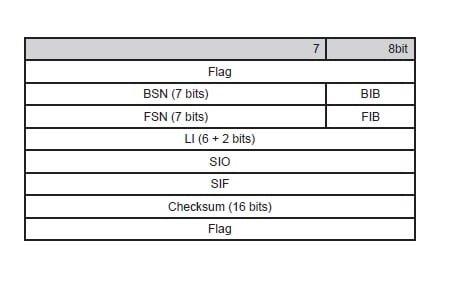
- BSN – Backward sequence number. Used to acknowledge message signal units which have been received from the remote end of the signalling link.
- BIB – Backward indicator bit. The forward and backward indicator bit together with the forward and backward sequence numbers are used in the basic error control method to perform the signal unit sequence control and acknowledgment functions.
- FSN – Forward sequence number.
- FIB – Forward indicator bit.
- LI – Length indicator. This indicates the number of octets following the length indicator octet.
- SIO – Service information octet.
- SIF – Signalling information field.
- Checksum – Every signal unit has 16 check bits for error detection.
- Service indicator – Used to perform message distribution and in some cases to perform message routing. The service indicator codes are used in international signalling networks for the following purposes:
- Sub-service field – The sub-service field contains the network indicator and two spare bits to discriminate between national and international messages.








