Broadband Audiovisual Communication – Systems and Terminals
Posted on |
BROADBAND AUDIOVISUAL COMMUNICATION – SYSTEMS AND TERMINALS
This Recommendation H.310 covers the technical requirements for the systems and terminals of broadband audiovisual communication services defined in H.200/AV.100-series Recommendations.
This H.310 defines both unidirectional and bidirectional broadband audiovisual terminals. The classification of H.310 terminals into different terminal types is based on audiovisual and ATM adaptation layer capabilities which are defined in 6.2. There are two classes of unidirectional terminals: Receive-Only Terminal (ROT) and Send-Only Terminal (SOT) classes.
In this H.310, bidirectional terminal types are referred to as Receive-and-Send Terminal (RAST) types. The definition of H.310 RAST terminals is based on the following interoperability principles:
- Interworking between H.310 RAST terminal types and other N-ISDN/B-ISDN (H.320/H.321) audiovisual terminals is mandatory.
- Interworking among the different H.310 RAST terminal types is also mandatory.
Three types of RAST terminals are defined: RAST-1, RAST-5, and RAST-1&5.
RAST-1 and RAST-1&5 terminals may be connected to public networks and customer premise networks (private networks), while RAST-5 terminals may only be connected to customer premise networks (private networks).
For interworking with H.320/H.321 terminals, all three RAST terminal types support common H.320 audiovisual modes. For interworking between RAST-5 terminals and RAST-1 and H.320/H.321 terminals, a gateway, that is not inside the public network but in the customer premises, between a B-ISDN and a customer-premises ATM network is needed to provide interoperability functions.
The video and audio coding and other technical aspects that are applicable to more than one distinct service are covered in H.200/AV.200-series Recommendations.
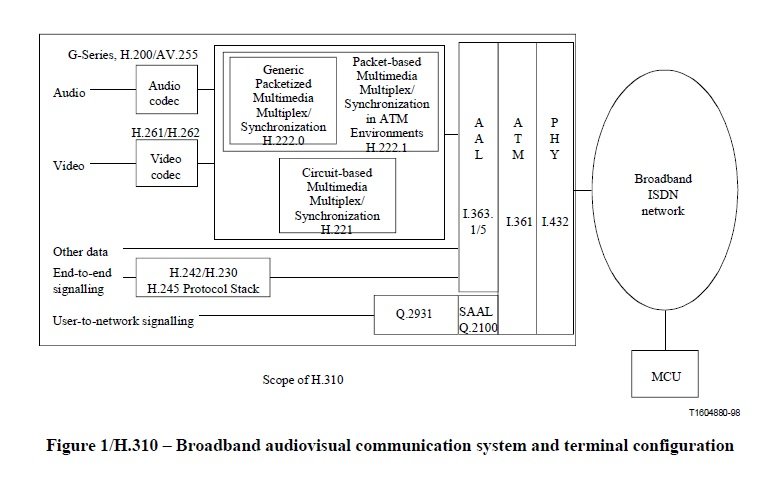
Figure 1 shows a generic broadband audiovisual communication system. It consists of terminal equipment, network, Multipoint Control Unit (MCU) and the constituent elements of the terminal equipment. The corresponding Recommendations are also identified.

All H.310 terminals are required to support H.245 as their communication control protocol so that they can support their intended services and interoperate with each other. Accordingly, H.310 terminals shall use the H.222.1 acknowledged procedures for the subchannel signalling.
It is important to note that the generic H.310 terminal shown in Figure 1 can represent any of the unidirectional or bidirectional terminal types defined in this Recommendation.
The definition of H.310 terminal types is intended for the support of the following applications:
- Conversational services (e.g. video conferencing and video telephony services).
- Retrieval services.
- Messaging services.
- Distribution services with the individual presentation by the recipient (e.g. video-on-demand services).
- Distribution services without the individual presentation by the recipient (e.g. broadcast TV services).
- Video transmission.
- Surveillance
System description
System configuration
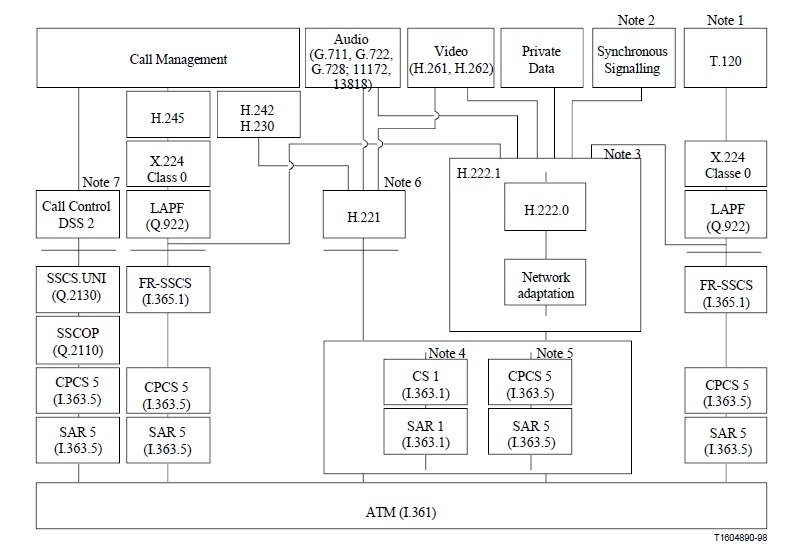
The interaction among the H.310 terminal capabilities is based on the protocol reference model
shown in Figure 2, which illustrates the protocol stacks for the audiovisual, data, call management (DSS 2 and H.245), and other control and indication signals that can be supported by the different terminal types of this Recommendation.
Recommendation | Title |
Q.2931 | User network interface layer 3 specifications for basic call/connection control |
Q.2941.1 | DSS 2 user-generated identifiers |
Q.2961 | Support of additional traffic parameters |
Q.2961.2 | ATM transfer capability coding in the broadband bearer capability information element |
Q.2962 | Negotiation of traffic and QoS parameters (during call/connection establishment) |
Q.2963 | Renegotiation/modification of traffic and QoS parameters (for already established calls/connections) |
Q.2964 | B-ISDN look-ahead |
Q.2971 | Point-multipoint call/connection control |
Q.298x | Multiconnection calls |
Terminal types
This Recommendation defines both unidirectional and bidirectional broadband audiovisual terminals.
The classification of H.310 terminals into different terminal types is based on audiovisual and AAL capabilities as summarized in Table 2.
| AAL | ||||
AAL 1 | AAL 5 | AAL 1& 5 | |||
Audiovisual transport | Unidirectional | ROT | ROT-1 | ROT-5 | ROT-1&5 |
SOT | SOT-1 | SOT-5 | SOT-1&5 | ||
Bidirectional | RAST | RAST-1 | RAST-5 | RAST-1&5 | |
Unidirectional terminal types (ROT and SOT)
Two classes of unidirectional terminals are defined: Send-Only Terminal (SOT) and Receive-Only Terminal (ROT).
Three types of H.310 unidirectional terminals are defined, based on their supported AALs, for each of the two classes. The H.310 defined unidirectional terminal types are:
- 310 ROT-1 and SOT-1 which support AAL 1;
- 310 ROT-5 and SOT-5 which support AAL 5;
- 310 ROT-1&5 and SOT-1&5 is a composite terminal supporting both AAL 1 and AAL 5.
Each of these terminal types shall support the H.310 native communication mode. The native communication mode consists of H.222.1, with ISO/IEC 11172-3 Layer 2, H.262 and H.245 as the audio, video and control protocols.
Each of these terminals may be connected to public B-ISDN and customer premise networks (private networks).
NOTE – Some pairs of a unidirectional terminal will not interwork with each other. This may be due to incompatible class, such as ROT-1 connecting with ROT-1&5, or due to incompatible type, such as ROT-1 connecting to SOT-5.
Bidirectional terminal types (RAST)
Three types of H.310 bidirectional receive and send terminals (RAST) are defined based on their
communication modes and supported AALs. The H.310 defined terminal types are:
- H.310 RAST-1 which supports AAL 1;
- H.310 RAST-5 which supports AAL 5;
- H.310 RAST-1&5 is a composite terminal supporting both AAL 1 and AAL 5.
Each of these terminal types shall support an H.310 native communication mode as well as an H.320/H.321 interoperation mode. Figure 3 depicts the protocol stacks for these two modes for each of the terminal types.
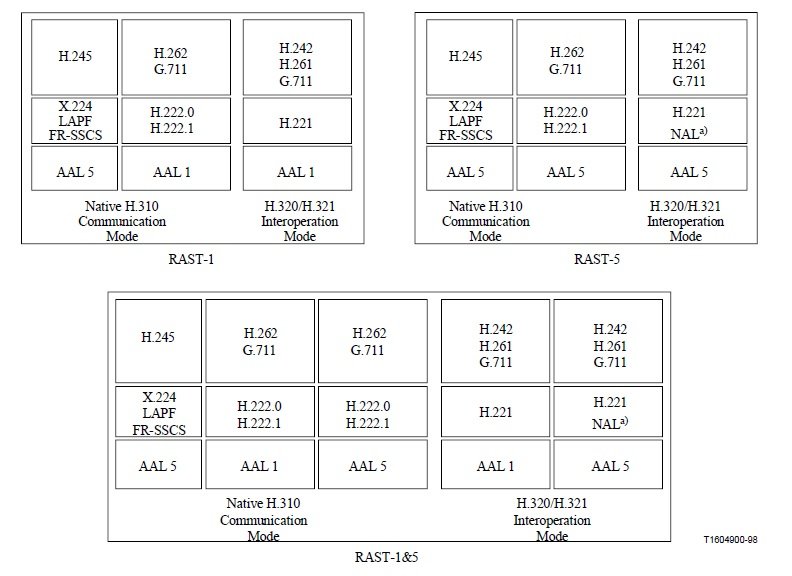
The H.310 RAST-1 terminal supports AAL 1. Its native H.310 communication mode consists of H.222.1, with G.711, H.262, and H.245 as the audio, video, and control protocols. Its H.320/H.321 interoperation mode supports the full H.321/Annex A protocol stack. The H.310 RAST-5 terminal supports AAL 5. Its native H.310 communication mode consists of H.222.1 with G.711, H.262, and H.245 as the audio, video and control protocols. Its H.320/H.321 interoperation mode supports the full H.321/Annex B protocol stack.
The H.310 RAST-1&5 is a composite of the RAST-1 and RAST-5 terminal types and supports all four modes described above.
The RAST-1 and RAST-1&5 terminals connect to public B-ISDN and customer premise networks (private networks) and can interwork with H.320 via an I.580 interworking unit and directly with H.321/Annex A terminals. The RAST-5 terminal connects to customer premise networks (private networks), can directly interwork with H.321/Annex B terminals and requires a gateway to interwork with H.320, H.321/Annex A and H.310 RAST-1 terminals. See clause 12 for interworking scenarios.
Terminal capabilities
The definition and classification of H.310 terminal types and their communication modes are based on the following capabilities:
- Audiovisual and Data;
- Network Adaptation;
- Signalling (both user-to-user and user-to-network).
A communication mode is defined as a combination of certain parameters of the above capabilities.
Based on the different capabilities of H.310 terminals, two classes of communication modes are specified:
- 320/H.321 interoperation modes;
- native H.310 communication modes.
Unidirectional H.310 terminals need only support native H.310 communication modes of operation, that is, unidirectional terminals may optionally support the H.320/H.321 interoperation modes.
At the start of the call, H.310 terminals shall identify the remote terminal type (H.320/H.321, H.310 bidirectional, etc.) via exchange of Q.2931 information elements, and shall use either H.245 or H.242 to perform capability exchange and other procedures.
This Recommendation mandates the support of particular functionalities by the different terminal types. However, this does not imply that a particular communication mode shall be used by that terminal type during a given communication session. For example, RAST terminals shall support H.261 video capabilities for interworking with H.320/H.321 terminals, but the use of H.261 in the native mode, that is, when H.222.1 is used, is optional.
The following subclauses describe mandatory and optional capabilities. Optional capabilities are included as guidelines for implementations and are in no way intended to be exhaustive lists of what may be implemented.
The use of the H.245 control channel
All H.310 terminals shall support H.245 messages and procedures in the native H.310 communication mode. The exact set of H.245 messages and procedures that are mandated in H.310 terminals, and their usage, are specified in this subclause.
The H.245 control channel carries end-to-end control messages governing the operation of the H.310 system, including capabilities exchange, opening and closing of logical channels, mode preference requests, round-trip-delay, maintenance loop and master-slave determination.
There shall be exactly one control channel in each direction within H.310 systems, which shall use the messages and procedures of Recommendation H.245. The H.245 control channel shall be set up at the beginning of communication, before the transmission of audiovisual information.
Recommendation H.245 specifies a number of independent protocol entities which support terminal-to-terminal signalling. A protocol entity is specified by its syntax (messages), semantics, and a set of procedures which specify the exchange of messages and the interaction with the user. H.310 terminals shall support the syntax, semantics and procedures of the following protocol entities, as specified in the following subclauses:
- Master-slave determination.
- Capabilities exchange.
- Logical channel signalling.
- Bidirectional logical channel signalling.
- Close logical channel signalling.
- Mode request.
- Round trip delay determination.
- Maintenance loop signalling.
- Specific commands and indications.
Figure 4 shows the interaction between the H.245 protocol entities and H.310.

All H.245 messages are conveyed by the underlying protocol stack, as specified in Annex A, which provides a reliable end-to-end transmission of H.245 messages using acknowledgement of correct receipt within each layer protocol.
H.310 terminals shall be capable of identifying all H.245 MultimediaSystemControlPDU messages and shall respond to all messages needed to realize required H.310 functions. H.310 terminals shall send the FunctionNotSupported message in response to the unrecognized request, response, command or the H.245 message which is not supported by the H.310 terminal.
Non-standard capabilities and control messages may be issued using the NonStandardParameter structure defined in Recommendation H.245. Note that while the meaning of non-standard messages is defined by individual organizations, equipment built by any manufacturer may signal any nonstandard message, if the meaning is known.
All timers defined in Recommendation H.245 should have periods of at least the maximum data delivery time allowed by the layer carrying H.245, including any retransmissions.

