SS7 / C7 Protocols: Signaling System # 7 for Telephony
Posted on |
SS7 / C7 Protocols: Signaling System # 7 for Telephony
Protocol Description
Signaling System #7 (SS7) is a telecommunications protocol suite defined by the ITU-T which is used by the telephone companies for interoffice signaling. SS7 uses out of band or common-channel signaling (CCS) techniques, which uses a separated packet-switched network for the signaling purpose. SS7 is known as C7 outside North America.
The primary function of SS7 / C7 is to provide call control, remote network management, and maintenance capabilities for the interoffice telephone network. SS7 performs these functions by exchanging control messages between SS7 telephone exchanges (signaling points or SPs) and SS7 signaling transfer points (STPs). Basically, the SS7 control network tells the switching office which paths to establish over the circuit-switched network. The STPs route SS7 control packets across the signaling network. A switching office may or may not be an STP.
The SS7 / C7 network and protocol are used for providing intelligent network services such as:
- basic call setup, management, and tear down
- wireless services such as personal communications services (PCS), wireless roaming, and mobile subscriber authentication
- local number portability (LNP)
- toll-free (800/888) and toll (900) wireline services
- 911, 411 services
- enhanced call features such as call forwarding, caller ID display, and three-way calling
- efficient and secure worldwide telecommunications
The current SS7 / C7 network, one of the largest data network in the world, connects together local telcos, cellular, and long-distance networks nationwide and worldwide.
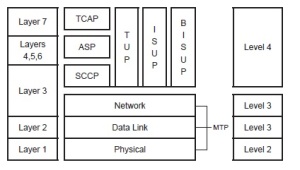
Protocol Structure
ASP | Application Service Part | ASP provides the functions of Layers 4 through 6 of the OSI model. |
BICC | Bearer Independent Call control protocol | BICC is a call control protocol based on ISUP used between serving nodes to support the ISDN services independent of the bearer technology and signaling message transport the technology used. |
BISUP | B-ISDN User Part | BISUP is an ATM protocol intended to support services such as high-definition television (HDTV), multilingual TV, voice and image storage and retrieval, video conferencing, high-speed LANs and multimedia. |
DUP | Data User Part | DUP defines the necessary call control, and facility registration and cancellation related elements for international common channel signaling by use of SS7 for circuit-switched data transmission services. |
ISUP | ISDN User Part | ISUP supports basic telephone call connect/disconnect between end offices. ISUP was derived from TUP but supports ISDN and intelligent networking functions. ISUP also links the cellular and PCS network to the PSTN. |
MAP | Mobile Application Part | MAP is used to share cellular subscriber information among different networks. |
MTP | Message Transfer Part | MTP crosses physical, data link and network layers. It defines what interface to be used, provides the network with the sequenced delivery of all SS7 message packets; and provides routing, message discrimination, and message distribution functions. |
SCCP | Signaling Connection Control Part | SCCP provides end-to-end routing. SCCP is required for routing TCAP messages to their proper database. |
TCAP | Transaction Capabilities Application Part | TCAP facilitates connection to an external database |
TUP | Telephone User Part | TUP is an analog protocol that performs basic telephone call connect and disconnect. |
 |  |  |  |  |  |