Videophone Service in Public Switched Telephone Network
Posted on |
Videophone Service in Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)
Introduction
Recommendation F.723 contains the description and network specific service requirements for videophone service in Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). The substance of this Recommendation complements the main body of the Supplement to Recommendation F.720, which deals with network independent service requirements for respective Low Bit Rate (LBR) videophone services provided in networks such as PSTN and digital mobile telecommunication networks across Low Bit Rate (LBR) channels. The difference between the service requirements in these two network domains stems from variations in access rates, mobility, the robustness of digital wireless transmission and different terminal environments. In addition to network-specific requirements, the network independent requirements for LBR videophone services and general requirements for all videophone services, included in Recommendation F.720, apply for the service as well.
Due to bandwidth and technical restrictions, the quality of service is limited and may be inadequate for many applications, in particular in the professional domain. Hence, it is essential that users of the service can utilize the reduced network capabilities as efficiently as possible with a flexibility in the channel allocation between voice, video, image and data.
This service can be used on a stand-alone basis or as part of a multimedia application. In the latter case, the same requirements apply.
General description
The general service description characteristics to all LBR videophone services is included in the Supplement of the F.720 Recommendation.
The service offers a real-time conversational two-way audiovisual end-to-end communication, comprising video, audio and optional2) in-band data transfer capabilities. As a rule, the audiovisual information is transferred along a single PSTN connection, based on LBR data channels. The aggregation of two PSTN connections for achieving increased overall capacity and QoS may be offered as an option (further studies are required).
For the video, the service should support the coding scheme defined by Recommendation H.263 and a spatial resolution conforming to QCIF and the terminal requirements covered by Recommendation H.324.
Basic functionalities
The basic functionalities, characteristic of videophone services in general, as well as those of the LBR videophone services, have to be supported.
The basic PSTN speech communication facility, i.e. that of an analogue telephone, must be included in the terminal so that the user shall be able to use the terminal as a normal telephone as well.
Concerning the fall-back, a slow repetition rate video mode, manually controllable from the receiving end, must be supported.
Dynamic channel allocation shall be provided as a mandatory system capability. Dynamic channel allocation is executed by means of a framing, synchronization and terminal negotiation mechanism in conformance to Recommendations H.245 and H.324 and other relevant ITU-T Recommendations.
Possible applications
In the consumer/residential segment the envisaged applications are real-time human-to-human interaction, based on the head-and-shoulders view, and remote surveillance and event monitoring e.g. for babysitting, security, as well as other non-conversational applications.
In business/institutional segment the foreseen applications are remote expert consultation, requiring audiovisual support, remote surveillance and recognition, remote troubleshooting, remote inspection and accessing videoconferences.
The above applications may be offered on a stand-alone basis or as part of a value-added multimedia application requiring extended terminal capabilities.
From the service point of view, the basic videophone terminal has to support QCIF only for the motion video. Some terminals, i.e. enhanced videophones may support also SQCIF3) format or at least they are capable of receiving SQCIF video frames.
Attributes and values
A.1 Low layer attributes
| Attributes | Values |
1 | Transfer mode | Circuit |
2 | Transfer rate | maximum 28.8 kbit/s (and beyond), under degraded network conditions may be less |
3 | Transfer capability | 3.1 kHz audio for Rec. V.34 (video telephony) 3.1 kHz speech for telephone mode (analogue telephony) |
4 | Structure | N/A |
5 | Establishment of communication | on demand |
6 | Symmetry | bidirectional symmetric |
7 | Configuration of call | point-to-point |
A.2 Access attributes
| Attributes | Values |
8 | Access channel and rate | in videophone mode: 5.3/6.4 kbit/s speech and 23.5/22.4 kbit/s video, or optionally in data mode 28.8 kbit/s or in speech and data mode: 5.3/6.4 kbit/s speech and 23.5/22.4 kbit/s data |
9.1 | Signalling access protocol, layer 1 | Rec. V.8/V.8 bis |
9.2 | Signalling access protocol, layer 2 | Rec. V.8/V.8 bis |
9.3 | Signalling access protocol, layer 3 |
|
9.4 | Information access protocol, layer 1 | Rec. H.223 |
9.5 | Information access protocol, layer 2 | Rec. H.245 |
9.6 | Information access protocol, layer 3 |
|
A.3 High layer attributes
| Attributes | Values |
10 | Type of user information | audio and video and/or data or plain data |
11 | Layer 4 protocol functions |
|
12 | Layer 5 protocol functions |
|
13 | Layer 6 protocol functions | Rec. G.723.1 for audio Rec. H.263 for video T.120-Series for data |
14 | Layer 7 protocol functions |
|
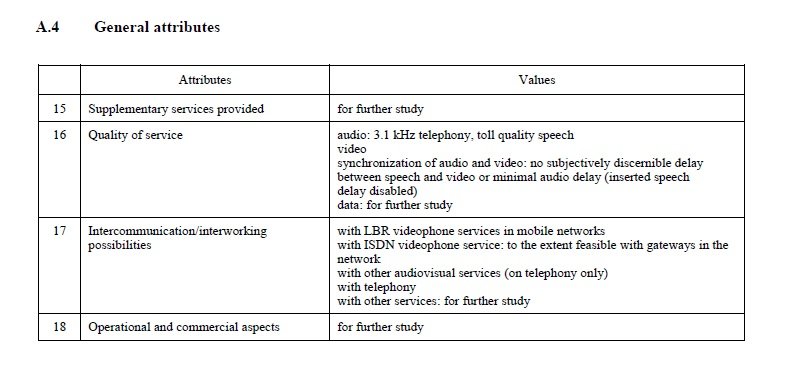
A.4 General attributes
| Attributes | Values |
15 | Supplementary services provided | for further study |
16 | Quality of service | audio: 3.1 kHz telephony, toll-quality speech video synchronization of audio and video: no subjectively discernible delay between speech and video or minimal audio delay (inserted speech delay disabled) data: for further study |
17 | Intercommunication/interworking possibilities | with LBR videophone services in mobile networks with ISDN videophone service: to the extent feasible with gateways in the network with other audiovisual services (on telephony only) with telephony with other services: for further study |
18 | Operational and commercial aspects | for further study |

